Skin testing was positive in 2 patients and intrapartum penicillin was not. Group B streptococcus GBS or Streptococcus agalactiae is one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality among newborns resulting in sepsis pneumonia and meningitis.

Penicillin Allergy Assessment In Pregnancy Safety And Impact On Antibiotic Use The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice
Penicillin or ampicillin during labor to prevent the spread of GBS to newborns during birth.

Group b strep uti treatment with penicillin allergy. Patients with no evidence of Type I allergy to penicillin may be treated with any cephalosporin or beta lactam antibiotic for infections of any severity. Clindamycin is recommended when a mother has a severe penicillin allergy. Which antibiotics treat group B strep UTI.
10-14 days total Table 3. For Group B Strep. A glycopeptide eg vancomycin is a suitable alternative in patients with penicillin allergy and will often be used in combination with gentamicin.
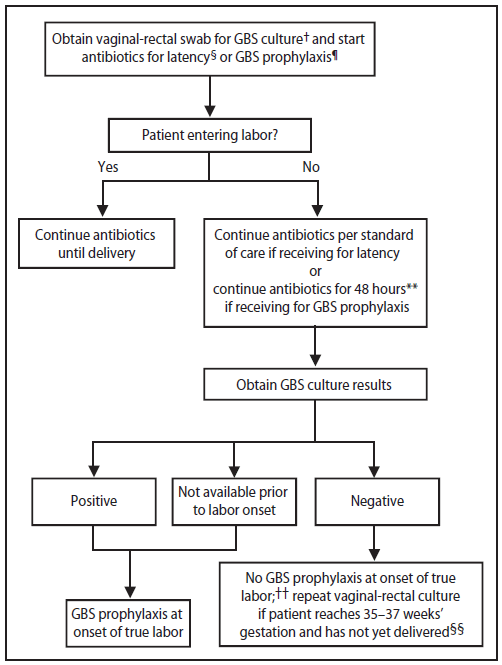
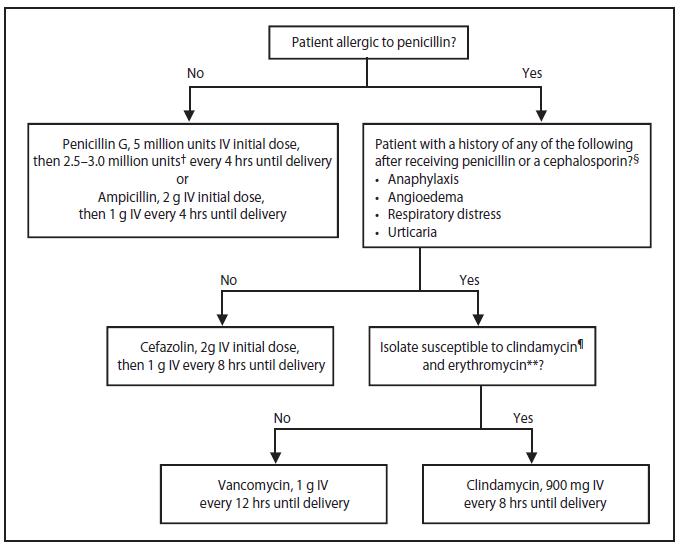
The antibiotic susceptibility profiles of 52 clinical isolates of GBS were evaluated to 12 antibiotics. If they have checked the group B strep sensitivities and it is sensitive to clindamycin then that is also an option. For a penicillin-allergic high anaphylaxis risk women with unknown GBS sensitivity results then vancomycin 1 gram IV every 12 hours until delivery should be administered.
However clindamycin-resistant germs cause. Treatment will depend on the kind of infection caused by GBS bacteria. V or vancomycin 2 gramsday I.
If skin testing was negative intrapartum antimicrobial prophylaxis with intravenous penicillin was administered. Clindamycin can also be used to treat adult GBS infections if the patient has a severe penicillin allergy. Group B streptococcus is generally susceptible to penicillin but E.
Of 28 patients with both GBS colonization and penicillin allergy 25 89 had negative skin testing to penicillin and received intrapartum penicillin for GBS prophylaxis without adverse reactions. Antibiotic sensitivities were determined using disk diffusion and microdilution methods according to the guidelines of the National Committee. Group B Strep Comes Back.
Aminoglycosides have little to no activity against group B streptococci when used alone but provide synergistic activity when combined with ampicillin or penicillin G. More than 40 of GBS infections. Table 2 17 18 lists oral antibiotics that are acceptable treatment choices.
Sometimes people with soft tissue and bone infections may need additional treatment such as surgery. There are two reasons why. Patients with symptoms suggestive of a Type I allergy should avoid cephalosporins and other beta-lactam antibiotics for mild or moderate infections when a suitable alternative exists.
It is concentrated poorly in urine metabolized primarily by the liver and is intended to treat. It is not suitable as monotherapy if meningitis is present. Risk factors administer an antibiotic IV penicillin 5 million units or ampicillin 2gm or other recommended alternative antibiotics as soon as the womans water breaks or labor begins.
The current recommendation for the treatment of Group B streptococcal endocarditis is penicillin 20 million unitsday I. If antepartum treatment of a urinary tract infection or bacteriuria is indicated clindamycin is not recommended as a treatment agent even in women allergic to penicillin. The CDC guidelines 2 are to use cefazolin during labor unless history is convincing for likely IgE mediated reaction and then alternatives would be clindamycin or vancomycin.
Penicillin remains the drug of choice in the treatment of Group B Streptococcus related urinary tract infections 16. The treatment during pregnancy is ideally a beta lactam amoxicillin penicillin or cephalosporin with clindamycin as an alternative if the strain is susceptible 1. IV therapy required until afebrile x 48 hrs then switch to PO antibiotics if appropriate Ceftriaxone 2g IV q 24hrs Gentamicin dosing per pharmacy Duration of treatment.
My last resort would be penicillin plus Benadryl given your prior allergy and given that their are other safe and reasonable options. Group B streptococcus GBS is a spherical bacteria that is commonly found in the digestive and lower genital tract of many individuals but may cause urinary tract infections UTI in newborns and in immunocompromised individuals 2. Penicillin VK 500 mg PO QID x 5-7 days Amoxicillin 500 mg PO TID x 5-7 days For pyelonephritis.
Vancomycin should be used prudently because it is not as effective for IAP as clindamycin and is a drug of last resort for gram positive. Ampicillin azithromycin cefamandole cefazolin ceftriaxone ciprofloxacin clindamycin erythromycin nitrofurantoin ofloxacin penicillin and vancomycin. For 28 days In the penicillin allergic patient cefazolin 6 gramsday I.
This is the only treatment that the CDC has found to be effective against GBS during labor. V for 28 days may be substituted. Penicillin tolerance has been reported with regard to a small subset of group B streptococci isolates and although it is of questionable clinical relevance MICMBC testing may be considered in refractory cases.
Parenteral therapy of 10 days duration is recommended for the treatment of bacteremia pneumonia. Doctors usually treat GBS disease with a type of antibiotic called beta-lactams which includes penicillin and ampicillin. In infants 1 month of age either cefotaxime or ceftriaxone may be used instead of combination therapy.
The common symptoms associated with GBS UTIs include frequent painful urination low grade fever and abdominal pain.

Group B Streptococcal Carriage Antimicrobial Susceptibility And Virulence Related Genes Among Pregnant Women In Alexandria Egypt Sciencedirect
Prevention Of Perinatal Group B Streptococcal Disease

Sample Algorithm For Group B Streptococcus Gbs Prophylaxis For Women Download Scientific Diagram
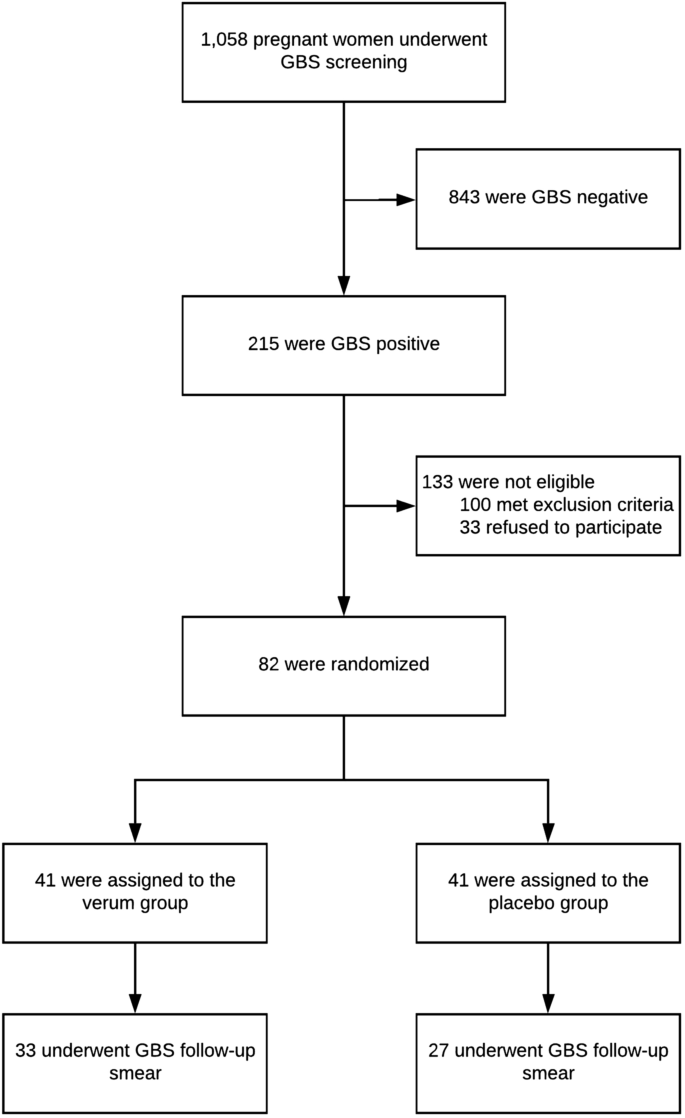
Oral Probiotics To Reduce Vaginal Group B Streptococcal Colonization In Late Pregnancy Scientific Reports